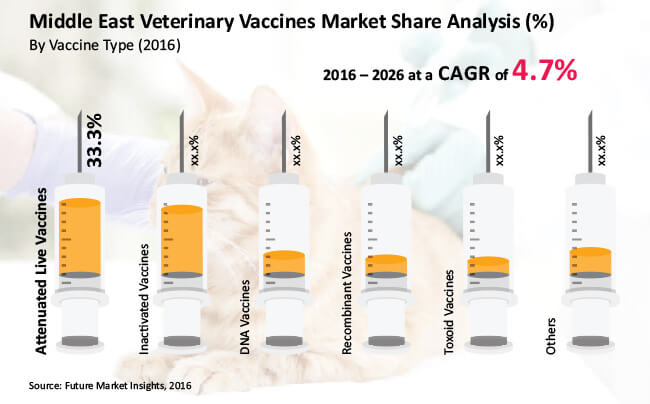
Attenuated live vaccines are expected to emerge as the dominant vaccine type segment over the forecast period
Attenuated live vaccines segment is the largest segment among the vaccine type segments, which was estimated to create close to US$ 90 Mn, or more than 30% share of the total market in 2016. By the end of 2026, attenuated live vaccines segment is projected to reach more than US$ 150 Mn, expanding at a CAGR of 5.8% over the forecast period. Greater adoption of live attenuated vaccines is expected to contribute to the attractive absolute $ opportunity of the segment. Attenuated live vaccines segment is expected to be the most lucrative in the MEA veterinary vaccines market with a market attractiveness index of 2.0.
Rising incidence of food borne and zoonotic diseases in MEA countries likely to fuel the demand for attenuated live vaccines
Rising incidence of food borne and zoonotic diseases in MEA countries is fuelling the demand in the attenuated live vaccines segment in the region. As the pattern of veterinary treatment is shifting from curative/reactive to preventive, the cost of a preventive treatment is much smaller and has far less side effects than reactive treatments that often lead to mass slaughter. This is the precise reason behind driving the growth of the attenuated live vaccines segment in the MEA region. Rebound of economic prosperity in MEA markets is expected to contribute towards increased demand for processed healthy meat products. This demands effective vaccination of livestock, especially in major animal farming and meat producing nations with a diversified herd in the region such as Sudan, Turkey, Egypt and KSA. Rising per capita disposable income levels are largely contributing to the rise in demand for processed food items. This is expected to drive the growth in demand for attenuated live vaccines in the poultry and livestock segments.
Request For Sample@ http://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/sample/rep-ma-3086
There are international guidelines on the usage of livestock identification and traceability systems (LITS) for better herd management, identifying zoonosis and managing animal health and incorporating food safety. However, most countries in the MEA region fail to implement proper LITS thereby affecting effective animal disease management. This is expected to fuel the demand for protective maintenance of animal health through early attenuated live vaccinations in order to avoid the spread of infectious diseases. The countries within the MEA region and Central Europe are increasingly dependent on live stock trading as a means of survival. Furthermore, in order to address chronic food insecurity in rural areas, animals are transferred from one place to another. This is fuelling demand for adequate vaccinations as an infection affecting one of the herds could easily spread to another and lead to mass losses. This factor is creating a positive impact on attenuated live vaccinations in the region.
Attenuated live vaccines are expected to witness increased demand throughout the forecast period in Jordan
The attenuated live vaccines segment is expected to witness a significant CAGR given greater adoption in commercial farms in the UAE veterinary vaccines market. Lower dosages and repetition are factors that are expected to contribute towards greater demand for attenuated live vaccines among all animal segments in Turkey. In Jordan, attenuated live vaccines are expected to witness increased demand throughout the forecast period. Lack of organised animal rearing and tracking practices hinder estimation of demand for attenuated live vaccines in Sudan.
Send An Enquiry@ http://www.futuremarketinsights.com/askus/rep-ma-3086
Scenario of Local Manufacturing and Veterinary Vaccine Registration
“The MEA region accounts for a vast livestock population; however, it is largely dependent on imports for the supply of adequate veterinary vaccines. Only six countries have the facility to produce vaccines locally. These include Egypt, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Syria and Turkey. Local produce acceptance is higher as regulatory authorities have relatively fewer requirements for local vaccines than imported ones. The time duration for imported vaccines to obtain the required registration is also longer. Only four countries follow the international norms of OIE although the OIE has not yet established official international standards in this respect.”
Browse Full Report@ http://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/middle-east-veterinary-vaccines-market
